Topics to Cover
Introduction
- What is a package
- What is composer
- Importance of packages
- Requireements to begin
Building the project
- initialize composer
- Namespaces
Publishing the Package
- Push to github
- Register it to packagist
- Add package tags
Introduction
What is a package?
Well packages are just reuseable codes that can be imported to other applications
What is composer?
composer is a php package manager. it help manage applications package and dependecies. was created in 2012 by Nils Adermann and Jordi Boggiano
Importance of packages?
They are used in building faster and scalable applications with lesser time and stress. instead of coding from scratch, you are only working on already developed, tested and trusted products, saving yourself time and stress. It also help in establishing a clean and easily understandable code base
Requirements to begin
To begi the journey of creating and publishing you very own php package, the following are very much required
- Signup to Github.
- Download Git.
- create a repository for your project.
- signup to packagist.
- download/install comoser on your machine (computer).
Building the package
After getting all the requirements ready, now you can start with the main package.
Initialize composer to your project
The first step in thia aspect, is to initialize composer to your project. And you can simply do that by running composer init on your terminal in your root directory. Fill all the neccesarry informations which include, the project name, description, authour name and email, dependacies etc. which will create a composer.json file with all the information in it, and a vendor folder with Autoload.php file in it.
Another way is by just creating a composer.json file manually with all the relevant information, then running composer install on the terminal.
Namespaces
Naamespaces are qualifers used in grouping classes to avoid collusions.
For example, you are creating a package that helps form validation, and you have a src directory containing 3 classes. One for strings validation and characters and symbols filther with characters count, another for email and unique keys validation, and the last for boolean, integer and floats validations. You can simply assign a validate namespace to the src folder.
you can do that by registering the namespaces in your composer.json file
"autoload": {
"psr-4": {
"src\\":"./validate"
}
},
where src is the directory name, and validate is the namespace
then you can include the below line of code to all your classes.
<?php
namespace validate;
If there is a directory in src for example called Exceptions, it would take the namwspace validate\Exceptions
Publishing the package
when you are done building the project, now it's time to publish. well this is the easiest part. you can acheive that with just this 3 steps:
Push code to github.
to push you code to github, just run the follow commad on your projrect root directory. And make sure you have git installed on your machine and have created a repository for your project on github
github repository link*
git init git commit -m "first commit" git branch -M main git remote add origin <repository url> git push -u origin maiRegister Package to Packagist
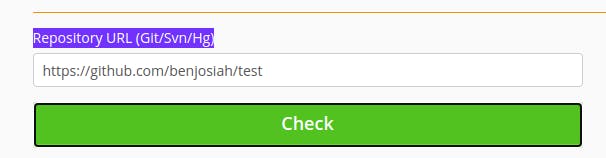
To publish the package, you have to register it with packagist.org. Visit the link, register and create an account. On your dashboard, click on Submit.
 Imput your github repo. link and click check, if it is available, click submit.
Imput your github repo. link and click check, if it is available, click submit.
Add Tags.
Tags simply help packagist track the package stability. in other words, it help you create updates an newer versions of the package. to create tags,go to github repository and click tags. add a tag starting for V1 or V0.1 or V0.01 depending on you. save change. and there you go you've successfully created a php package.
Usage
To use in your application or any other project you're working on or have other developers use in their project, simply run composer require <package name> <version> on your termital in your root directory of the project.
P.S: not specifying the version would install the latest version by default
checkout packagist.org/about to get more information.

